Министр энергетики Журабек Мирзамахмудов объяснил, почему Узбекистан принял решение о строительстве атомной электростанции (АЭС). По его словам, атомная энергетика сегодня является одной из самых безопасных отраслей благодаря учёту уроков прошлых аварий, таких как инциденты на Фукусиме и Чернобыле. В современных АЭС вероятность радиационной угрозы сведена к минимуму даже при внешних и внутренних воздействиях.
Безопасность в деталях
Мирзамахмудов в ходе беседы в подкасте «Лолазор» подчеркнул, что на современных АЭС предусмотрены автономные системы, способные работать в течение 72 часов без вмешательства человека в случае аварии. Эти системы обеспечивают охлаждение реактора, предотвращение процесса расплавления и безопасное стеклование расплава, что значительно снижает риск радиационного выброса. Он отметил, что даже при самых неблагоприятных условиях вероятность катастрофы минимальна благодаря многоуровневым системам безопасности.
«Даже в случае отключения электропитания, система охлаждения автоматически активируется и запускает процесс, напоминающий работу ловушки расплава. Однако современные реакторы значительно безопаснее: они способны предотвратить катастрофу и обезвредить потенциальные угрозы,» – пояснил министр.
Преимущества маломощных АЭС
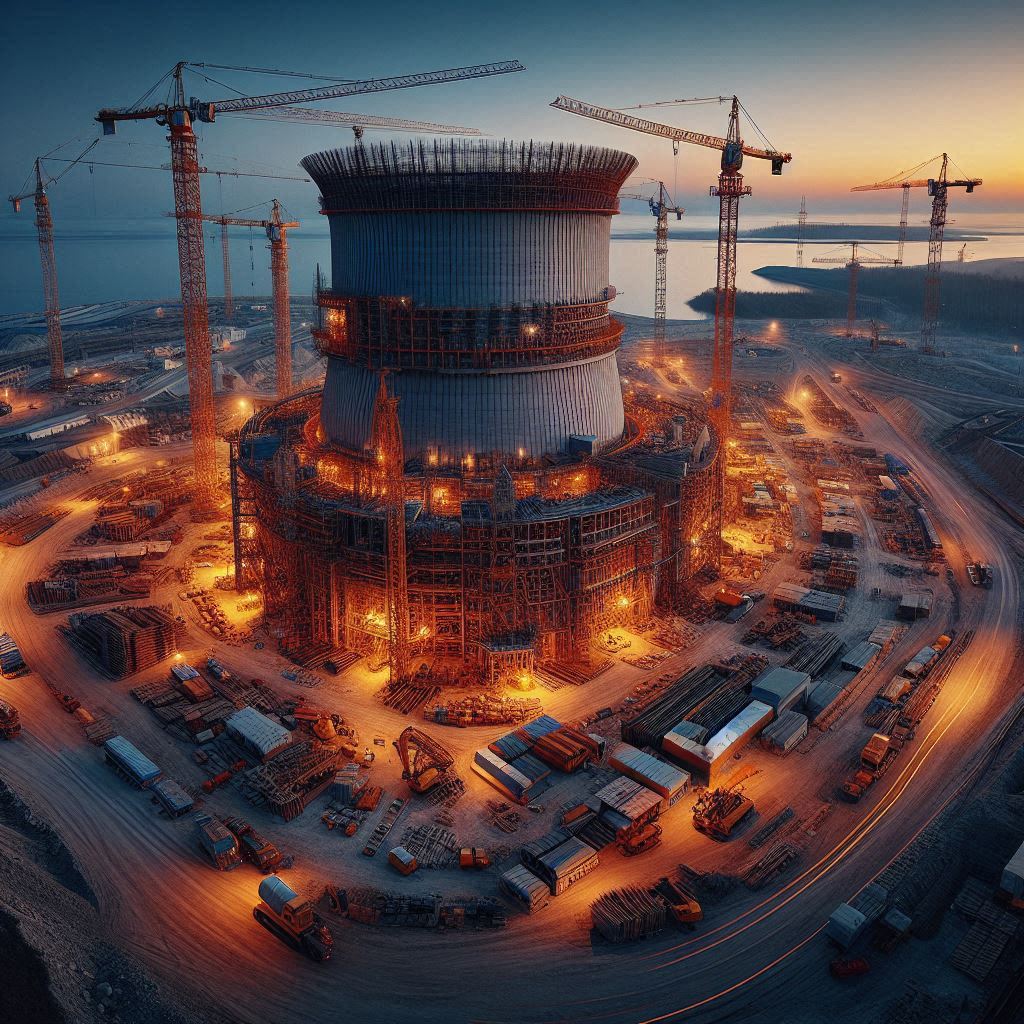
Будущая АЭС в Джизакской области будет иметь мощность 330 МВт, состоящую из шести реакторов мощностью 55 МВт каждый. «Росатом» выступит генеральным подрядчиком строительства, к которому также будут привлечены местные компании. Проект предусматривает использование новейшей российской технологии — водо-водяного реактора РИТМ-200Н, адаптированной для наземного размещения.
РИТМ-200Н имеет тепловую мощность 190 МВт, электрическую мощность 55 МВт и рассчитан на срок службы до 60 лет. Эта технология была протестирована на российских атомных ледоколах, работающих в суровых условиях Арктики, что подтверждает её надёжность и устойчивость.
По словам экспертов, маломощные атомные станции, такие как АЭС в Джизаке, имеют ряд ключевых преимуществ. Они отличаются более короткими сроками строительства благодаря компактности и меньшим объёмам работ. Согласно данным МАГАТЭ, во всём мире разрабатывается около 50 проектов маломощных АЭС, что подчёркивает их важность для дальнейшего развития мировой атомной энергетики.
Высокие стандарты безопасности
Одним из важнейших аспектов маломощной АЭС является её высокая степень безопасности. Станция будет оборудована многоуровневыми системами и барьерами-оболочками. Эти системы включают как активные (зависящие от внешних источников энергии), так и пассивные системы безопасности, которые работают без необходимости в энергии. Такая комбинация обеспечивает максимальный уровень безопасности и предотвращает вероятность аварий.
Кроме того, несколько уровней защитных барьеров, встроенных в конструкцию станции, исключают возможность выброса радиоактивных веществ в окружающую среду, что делает АЭС максимально безопасной для экологии.